Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Category
Inflammatory, Lung
REVIEWED BY
Our Biomedical Scientist
Reviewed based on
Literature Discussion & Clinical Trials
Last update
August 2020
What is COPD
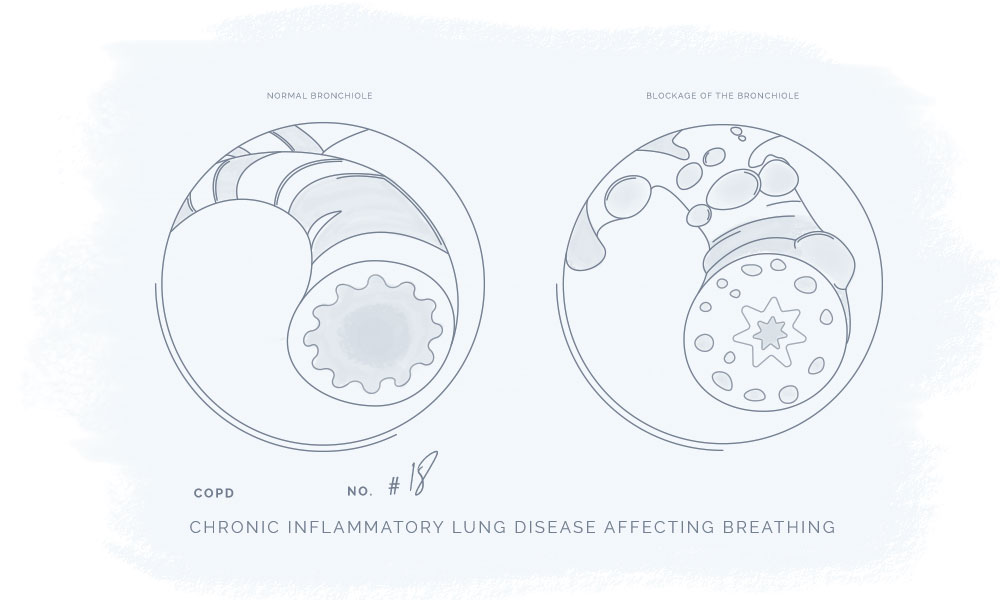
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease most often brought on by long-term exposure to irritating gases or smoking. COPD can lead to breathing difficulties and other severe /fatal conditions such as lung cancer.1
Symptoms
Symptoms of COPD usually do not appear before the disease has entered an advanced state with significant lung damage. The symptoms worsen over time, especially if exposure to e.g. smoking continues and they may include:1
- Tightness in the chest
- Shortness of breath and wheezing
- A chronic cough that may produce clear, white, yellow, or greenish mucus/sputum
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Unintended weight loss
- Swelling in legs, feet, and ankles
- General lack of energy
Cause
In developed countries, COPD can primarily be caused by tobacco smoking, whereas in developing countries, exposure to fumes can often lead to the development of COPD.
Normally the lungs depend on the natural elasticity of the bronchial tubes, whereas COPD leads to the loss of elasticity in the lungs and over-expansion, which results that there is some air left when people exhale.1
There are 2 types of COPD
- Emphysema
The disease leads to the destruction of the walls and elastic fibers of the air sacs. Small airways collapse during exhalation, resulting in impaired airflow out of the lungs. - Chronic bronchitis
- Inflammation and narrowing affect the bronchial tubes and more mucus is produced by the lungs, which can further lead to blockage of the narrowed tubes.
The connection between Cannabinoids & Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Studies find that CBD and THC may have great therapeutic potential and may be used to help treat COPD. CBD and THC are well-known cannabinoids, however, they do not have the same psychoactive effects. THC is psychoactive while CBD does not possess psychoactive effects. According to WHO guidelines, the cannabidiol CBD is generally well tolerated with a good safety profile.
Preclinical evidence proposes that the cannabinoids THC, CBD, and THCV may be therapeutic in the treatment of COPD as cannabinoids possess anti-inflammatory properties that may help relieve the symptoms of the disease.2
The literature discussion is an overview of the published results from scientific studies investigating if and how cannabinoids can be beneficial in the treatment of COPD. The overview will be updated regularly to ensure the newest and most accurate information.
THC and CBD activated through CB1 may reduce bronchoconstriction, inflammation, and coughing
In a study with guinea pigs, plant cannabinoids such as THC, CBD, CBC , CBG, CBDA, and THCV were used to assess whether they have any effect on bronchoconstriction, inflammation, and coughing. It was found that all three parameters were reduced by THC via activation of CB1 and CB2. CBD inhibited coughing and THCV decreased inflammatory leucocyte recruitment, whereas other cannabinoids did not produce any effect.3
CBD may inhibit lung inflammation
In the ovalbumin rat model of asthma, serum levels of all analyzed cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-6, and TNF-α but not IL-10 were decreased upon treatment with CBD (5 mg/kg, i.p.). This suggests that CBD may have a therapeutic potential in inhibiting lung inflammation.4
In the LPS mouse model of lung inflammation, pparγ-dependent G-CSF secretion by mast cells and subsequent myeloid-derived suppressor cell mobilization were induced by CBD (20 mg/kg i.p.).5
Anandamide may suppress COPD symptoms
In human patients, anandamide was observed to be involved in suppressing bronchospasms and coughing via activation of CB1 receptors.6
Clinical trials are research studies that examine new treatments and evaluate their effects on human health outcomes.
THC and CBD may relieve symptoms of COPD
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled crossover study involved five normal and four COPD participants to evaluate the effect of cannabinoids. It was found that cannabinoids (THC/CBD) do not ameliorate lung function but decrease the amount of discomfort related to COPD.7
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/copd/symptoms-causes/syc-20353679
- https://ghmedical.com/endocannabinoid-system/diseases/copd
literature - Makwana et al., (2015). ” The effect of phytocannabinoids on airway hyperresponsiveness, airway inflammation and cough. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25655949/
- Vuolo et al., (2015). ” Evaluation of Serum Cytokines Levels and the Role of Cannabidiol Treatment in Animal Model of Asthma. Mediators Inflamm. 2015, 538670”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26101464/
- Hegde et al., (2015). ” Critical Role of Mast Cells and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ in the Induction of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells by Marijuana Cannabidiol In Vivo. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 194, 5211–5222”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25917103/
- Calignano et al., (2000). ” Bidirectional control of airway responsiveness by endogenous cannabinoids. Nature 408, 96–101”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11081515/
clinical - Pickering et al., (2011). ”Cannabinoid effects on ventilation and breathlessness: a pilot study of efficacy and safety. Chron. Respir. Dis. 8, 109–118”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21436223/
CANNABINOIDS & RECEPTORS
Below you find the plant cannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors, and endocannabinoids that are associated with the potential therapy.
If you have any further information relevant to the connection between COPD and cannabinoids or find any of the information inaccurate, outdated or incomplete please contact us here.

