Cellular Biology
The Endocannabinoid System Safeguards Balance in your Body

The Endocannabinoid
System (ECS)
Endogenous Cannabinoids Produced Naturally by the Body
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is found in all mammals. ECS is critical for communication in the body. Thus, the reason why we are not just a mass of cells, but precisely designed, functional human beings is the ECS.
This unique system is involved in many critical functions of our body, such as cell division processes, and brain, nervous- and immune systems. It plays a crucial role in our general health as well as our ability to fight off a number of health-related conditions.
The ECS is made up of cannabinoid receptors, endocannabinoids and enzymes. Anandamide (ANA) and 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) are the best-studied endocannabinoids produced in our body that help regulate and balance many processes in the body.
The ECS is Comprised of
1. Endogenous Cannabinoids
Produced naturally by the body
2. Synthetic Cannabinoids
Chemicaly produced and distributed by the medical industry
3. Phyto/Plant Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant
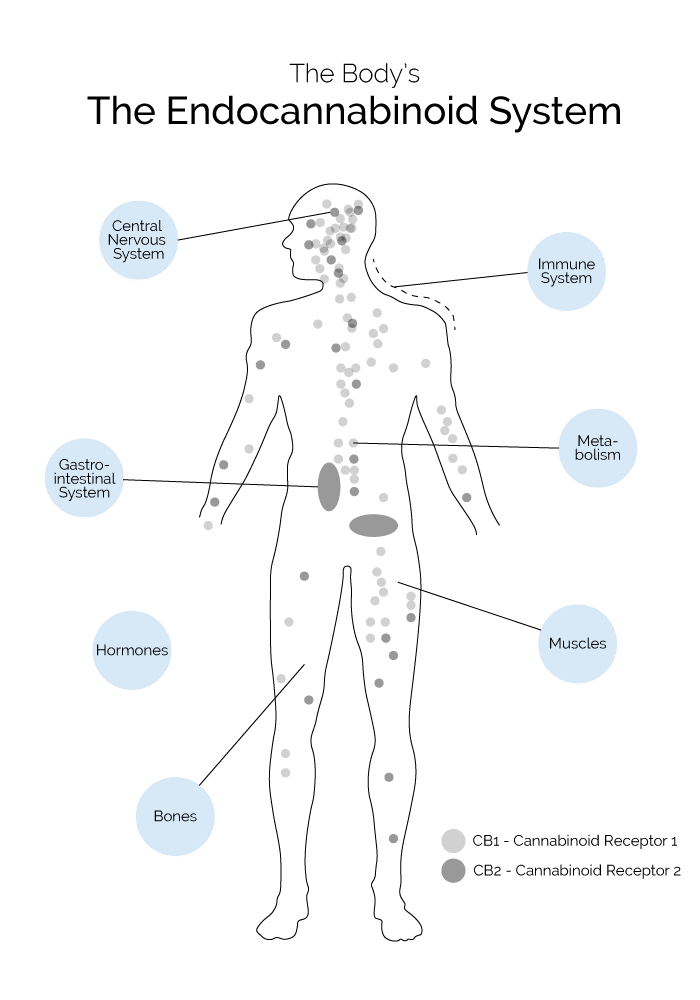
Cannabinoid Receptors
Cannabinoid receptors are located on the surface of cells in your body and they “listen” to conditions outside the cell. They transmit information about altered conditions to the inside of the cell and initiate relevant cellular responses.
There are two main cannabinoid receptors: CB1 and CB2. These are not the only cannabinoid receptors, but were he first to be discovered and remain the best studied.
CB1 and CB2 receptors are key players in the ECS. CB1 receptors are more prevalent in the central nervous system, including neurons in the brain. In contrast, CB2 receptors are more abundant outside the nervous system, including cells of the immune system.
Endo-
cannabinoids
Endocannabinoids, also called endogenous cannabinoids, are molecules made by your body. They’re similar to plant cannabinoids, but they are produced by your body.
By far the two key endocannabinoids identified are:
- Anandamide (AEA)
- 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG)
These molecules help to keep our internal functions running smoothly. The body produces them as needed.
Distance running or other exercises that require stamina can lead to a feeling known as “runners high”, which is linked to decreased anxiety and pain, an increased sense of relaxation and euphoria. The levels of Anandamide and β-endorphin are found to be abundantly increased in the plasma of humans and mice after long-distance running.
Metabolic Enzymes
Metabolic enzymes include FAAH and MAGL that are responsible for the degradation of endocannabinoids. FAAH is responsible for breaking down ANA, meanwhile MAGL is responsible for breaking down 2-AG.
These enzymes ensure that endocannabinoids are present when needed and for how long they are needed. This process separates endocannabinoids from many other molecular signals in your body, such as hormones or classic neurotransmitters, which can persist for many seconds or minutes, or be packed and stored for later use.
The Endocannabinoid System Safeguards
Share Similarities to Cannabinoids Found in the Cannabis Plant
The ECS Maintains Balance or Homeostasis in your Body. It plays a role in many critical functions of your body such as energy supply, brain activity, cell division, and immunity to maintain our bodies’ structural and functional integrity. If the ECS fails to work properly the interactions and communication between the different organs will be interrupted which can cause diseases, e.g.:
Metabolic Disorders
Such as obesity, anorexia, diabetes or cancer
Detegenerative Disorders
Such as Alzheimer’s
Such as epilepsy or migraine
Such as arthritis, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, etc.
The Human Body's Own Cannabinoids
The Biochemical Balance in your Body
Phytocannabinoids
Phytocannabinoids, produced by the cannabis plant, can bind to the endocannabinoid receptors in the human body alike endocannabinoids do. Thus, addition of natural and plant-based cannabinoids to your treatment or prevention routine can improve the functions of the ECS and help your body regain balance.
Plant cannabinoids
Plant cannabinoids can be used to enhance and optimize our endocannabinoid system, and thus anticipate, prevent, or even help fight the above listed (and many more) diseases.
Efficacy of Plant Cannabinoids in Treatment
The Use of Cannabis May Exhibit Positive Effects in Numerous Health-Related Conditions.
The use of cannabis may exhibit positive effects in numerous health-related conditions. Patients report many benefits of CBD including relieving inflammation, insomnia, anxiety, spasticity, and pain. CBD may also help relieve certain symptoms associated with cancer and side effects of cancer treatment.
The therapeutic effects of cannabis are still under investigation and many clinical trials are being performed. One of the more comprehensive studies has been performed by the National Academy of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine by Harvard Medical School, which found substantial evidence that cannabis/cannabinoids may be effective for treating chronic pain and inflammation. The committee concluded their finding in 2017 based on reviewing 10,000 studies from the past two decades and weighed the strength of the evidence for nearly two dozen health conditions that scientists have studied.
In our disease section, we review some of the above studies. The evaluation is performed by a comparison with current clinical trials and literature in the field, including PubMed (US National Library of Medicine, NIH) and SpringerLink (the world’s most comprehensive online collection of scientific, technological, and medical journals).
REFERENCES
The information about cellular biology is based on work from GH Medical’s extensive database collected and contributed to by industry-independent scientists and experts within the field of research and/or treatment with cannabinoids.